#158 The hypothetical machine of Figure
The hypothetical machine of Figure - Computer Science
ChemistryExplain daily providing Q&A content “#158 The hypothetical machine of Figure" in Computer science, Ba computer science, Berkeley computer science, Computer science associate degree jobsGet the Free Online Chemistry Q&A Questions And Answers with explain. To crack any examinations and Interview tests these Chemistry Questions And Answers are very useful. Here we have uploaded the Free Online Chemistry Questions. Here we are also given the all chemistry topic.
ChemistryExplain team has covered all Topics related to inorganic, organic, physical chemistry, and others So, Prepare these Chemistry Questions and Answers with Explanation Pdf.
For More Chegg Questions
Free Chegg Question
The hypothetical machine of Figure 3.4 also has two I/O instructions:0011 = Load AC from I/O
0111 = Store AC to I/O
In these cases, the 12-bit address identifies a particular I/O device. Show the program execution (using the format of Figure 3.5) for the following program:
1. Load AC from device 5.For More Chemistry Notes and Helpful Content Subscribe Our YouTube Chanel - Chemistry Explain
2. Add contents of memory location 940.
3. Store AC to device 6.
Assume that the next value retrieved fromdevice 5 is 3 and that location 940 contains a value of 2.
Example of Program Execution (contents of memory and registers in hexadecimal)
Free Chegg Answer
Program execution as per figure 3.5 from textbook:
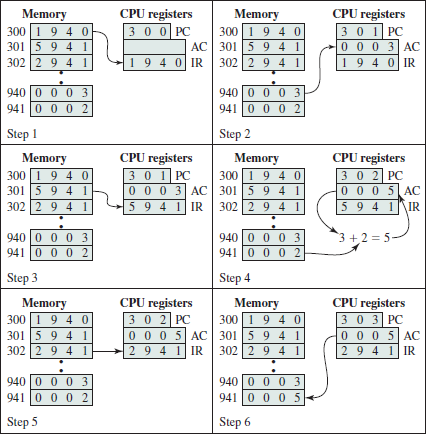
Step 1: Instruction Register (IR) 3005.
3005.
Step 2: Accumulator (AC) 3
3
Step 3: Instruction Register (IR) 5940
5940
Step 4: Accumulator (AC) 5 (3 +2)
5 (3 +2)
Step 5: Instruction Register (IR) 7006
7006
Step 6: Device 6 Accumulator (AC)
Accumulator (AC)
Step 1: Instruction Register (IR)
 3005.
3005.Step 2: Accumulator (AC)
 3
3Step 3: Instruction Register (IR)
 5940
5940Step 4: Accumulator (AC)
 5 (3 +2)
5 (3 +2)Step 5: Instruction Register (IR)
 7006
7006Step 6: Device 6
 Accumulator (AC)
Accumulator (AC)
Explanation:
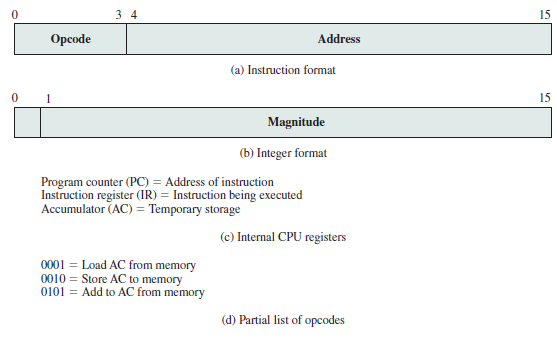
• Instruction register (IR) is the one which stores instruction currently being executed or decoded.
• Program counter (PC) is the one that holds address of the instruction being executed at current time.
• 12 bits is used to specify the address and 4 bits in the IR indicates accumulator to be loaded.
Let the contents of memory location be,
• 300 : 3005
• 301 : 5940
• 302 : 7006
• Instruction register (IR) is the one which stores instruction currently being executed or decoded.
• Program counter (PC) is the one that holds address of the instruction being executed at current time.
• 12 bits is used to specify the address and 4 bits in the IR indicates accumulator to be loaded.
Let the contents of memory location be,
• 300 : 3005
• 301 : 5940
• 302 : 7006
Step 1:
In step1 the “Program Counter” holds the value of “300” and “Instruction register” holds contents of address “300” that is “3005”.
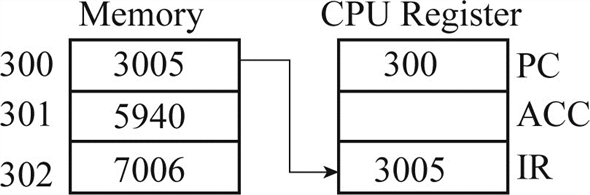
In step1 the “Program Counter” holds the value of “300” and “Instruction register” holds contents of address “300” that is “3005”.

Step 2 & Step 3:
The content of address location “005” is moved to the accumulator and Instruction register holds the value “5940
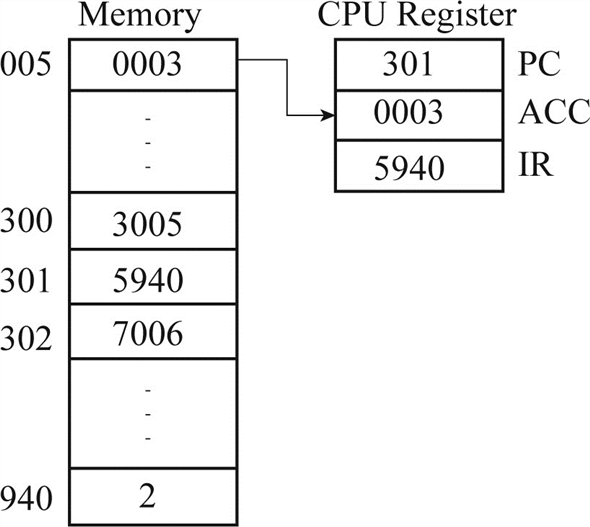
The content of address location “005” is moved to the accumulator and Instruction register holds the value “5940

Step 4:
Add contents of Accumulator with contents of address “940” and stored back to accumulator.
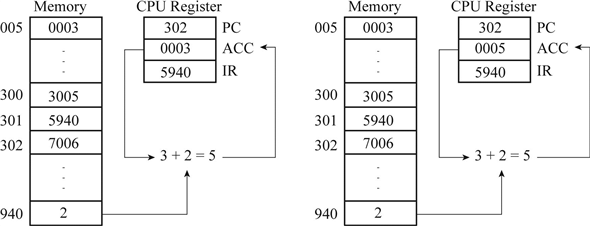
Add contents of Accumulator with contents of address “940” and stored back to accumulator.

Step 5:
The next instruction (7006) is fetched from location 302 and PC is incremented.
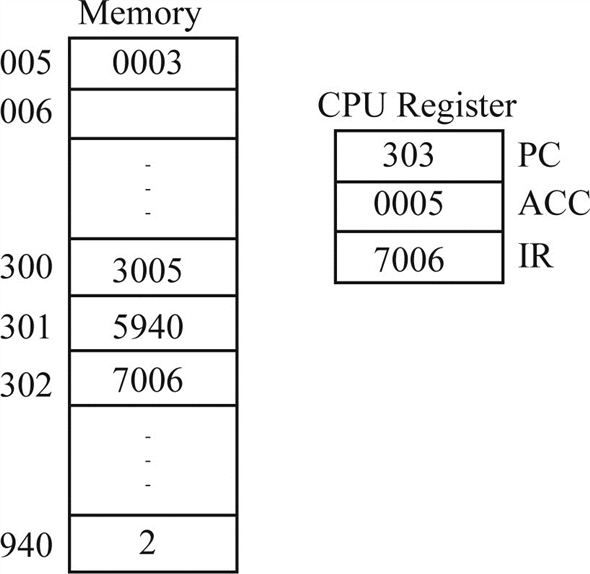
The next instruction (7006) is fetched from location 302 and PC is incremented.

Step 6:
The contents of the AC are stored in location 006
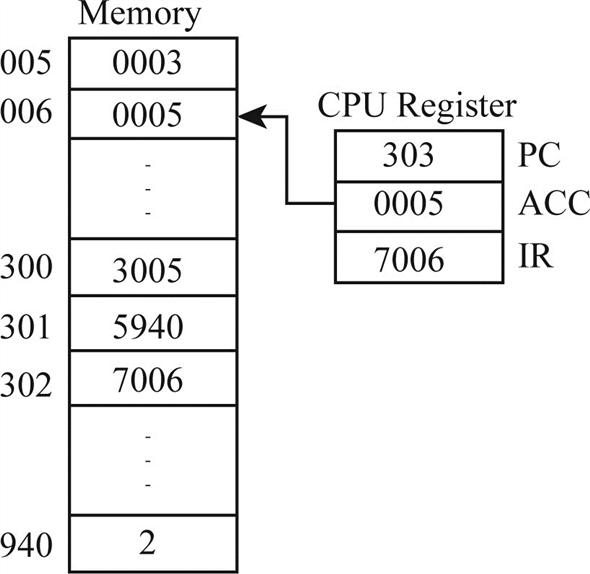
The contents of the AC are stored in location 006

Thus, execution steps for the given problem according to figure 3.5 from text book is done.
Labels: Chegg, Free Chegg Answer, Q&A Computer Science


0 Comments:
Post a Comment
Subscribe to Post Comments [Atom]
<< Home