#493 The magnitude of the net force exerted
The magnitude of the net force exerted - Physics
ChemistryExplain daily providing Q&A content “#493 The magnitude of the net force exerted" in Physics, Ap physics 1 practice test, Best colleges for physics, Best physics books, Best physics schools
Get the Free Online Chemistry Q&A Questions And Answers with explain. To crack any examinations and Interview tests these Chemistry Questions And Answers are very useful. Here we have uploaded the Free Online Chemistry Questions. Here we are also given the all chemistry topic.
ChemistryExplain team has covered all Topics related to inorganic, organic, physical chemistry, and others So, Prepare these Chemistry Questions and Answers with Explanation Pdf.
For More Chegg Questions
Free Chegg Question
The magnitude of the net force exerted in the x direction on a 3.90-kg particle varies in time as shown in the figure below.
(a) Find the impulse of the force over the 5.00-s time interval. I = ? (N · s)
(b) Find the final velocity the particle attains if it is originally at rest. Vf = ? (m/s)
(c) Find its final velocity if its original velocity is -3.10 i m/s. Vf = ? (m/s)
(d) Find the average force exerted on the particle for the time interval between 0 and 5.00 s. Favg = ? (N)
Free Chegg AnswerFor More Chemistry Notes and Helpful Content Subscribe Our YouTube Chanel - Chemistry Explain
Free Chegg Answer
General guidance
The concepts used to solve this question is the impulse
Initially, draw the graph and then the impulse is determined by calculating the area under the graph. Later use the impulse to find the initial and final velocities of the particle. At last use the relation between impulse, force and time to determine average force acting on the particle.
Impulse:
Impulse is a vector quantity and has both magnitudes as well as direction. It is defined as the product of the force acting on the particle and time interval at which force is acting on the particle.
The magnitude of the impulse is,
I=FΔt
Here, F is the force acting on the particle and Δt is the time interval.
The impulse is also defined as the change in momentum of the particle.
I=mΔv
Here, m is the mass of the particle and Δv is the change in velocity.
Step 1 of 4
(a)
The graph between the force and the time is drawn below.
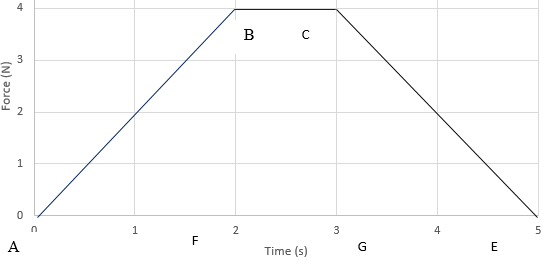
The area of the graph gives the impulse.
Therefore,
I=Area(ABF)+Area(BCFG)+Area(CEG)=(21)(4N)(2s)+(4N)(1s)+(21)(4N)(2s)=2(4N⋅s)+4N⋅s=12N⋅s
The impulse of the force over the time interval 5s is 12N⋅s
Explanation | Common mistakes | Hint for next step
The area under the graph gives the impulse. The units of the impulse is N⋅s . The area of the graph is formed by two triangles and one rectangle. The total area of the graph is the sum of the area of two triangles and one rectangle.
Step 2 of 4
(b)
The final velocity of the particle is,
I=m(vf−vi)
The above equation is modified as,
vf=mI+vi …… (1)
Here, vi is the initial velocity of the particle.
Substitute 12N⋅s for I , 3.90kg for m and 0m/s for vi in the equation (1).
vf=mI+vi=3.90kg12N⋅s+0m/s=3.076m/s
The final velocity of the particle is 3.076m/s
Explanation | Common mistakes | Hint for next step
The particle starts from rest and therefore the initial velocity of the particle is zero. Hence, the final velocity of the particle depends on the impulse and mass of the particle.
Step 3 of 4
(c)
The final velocity of the particle is,
vf=mI+vi …… (2)
Here, vi is the initial velocity of the particle.
Substitute 12N⋅s for I , 3.90kg for m and −3.10m/s for vi in the equation (2).
vf=mI+vi=3.90kg12N⋅s−3.10m/s=−0.024m/s
The final velocity of the particle is −0.024m/s
Explanation | Common mistakes | Hint for next step
The initial velocity of the particle is known and therefore by using the impulse equation, the final velocity of the particle has been determined.
Step 4 of 4
(d)
The average force exerted on the particle is,
F=ΔtI …… (3)
Substitute 12N⋅s for I and 5s for Δt in the equation (3).
F=ΔtI=5s12N⋅s=2.4N
The average force exerted on the particle is 2.4N
Explanation | Common mistakes
The force acting on the particle is,
F∝I
And,
F∝Δt1
Hence, from the above relations, the average force acting on the particle is directly proportional to the impulse. Hence, with an increase in the impulse, the average force exerted on the particle will increase.
Answer
The impulse of the force over the time interval 5s is 12N⋅s
The final velocity of the particle is 3.076m/s
The final velocity of the particle is −0.024m/s
The average force exerted on the particle is 2.4N
Labels: Chegg, Free Chegg Answer, Q&A Physics


0 Comments:
Post a Comment
Subscribe to Post Comments [Atom]
<< Home