#238 Laboratory experiments designed to measure
Laboratory experiments designed to measure - Math
ChemistryExplain daily providing Q&A content “#238 Laboratory experiments designed to measure" in Bridges math curriculum, Dr mather, Carnegie math, 10th maths, 10th grade math problems, Math
Get the Free Online Chemistry Q&A Questions And Answers with explain. To crack any examinations and Interview tests these Chemistry Questions And Answers are very useful. Here we have uploaded the Free Online Chemistry Questions. Here we are also given the all chemistry topic.
ChemistryExplain team has covered all Topics related to inorganic, organic, physical chemistry, and others So, Prepare these Chemistry Questions and Answers with Explanation Pdf.
For More Chegg Questions
Free Chegg Question
Laboratory experiments designed to measure LC50 (lethal concentration killing 50%of the test species) values for the effect of certain toxicants on fish are run by two different methods. One method has water continuously flowing through laboratory tanks, and the other method has static water conditions. For purposes of establishing criteria for toxicants, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) wants to adjust all results to the flow-through condition. Thus, a model is needed to relate the two types of observations. Observations on toxicants examined under both static and flow-through conditions yielded the data in the accompanying table (measurements in parts per million, ppm). Fit the model Y = β0 + β1 x + ε.
What interpretation can you give to the results?
b Estimate the flow-through value for a toxicant with an LC50 static value of x = 12 ppm.
For More Chemistry Notes and Helpful Content Subscribe Our YouTube Chanel - Chemistry Explain
Free Chegg Answer
-
Step 1 of 8
To fit the model
to the given data.
Here
is the random error component with
.
-
Step 2 of 8
The least squares estimates of the coefficients
and
, say,
and
, given by
where,
and
-
Step 3 of 8
Consider the following table:
Table 1: Calculation for finding the coefficients
Toxicant
LC50
Flow-Through
(
)
LC50
static
(
)
1
23.00
39.00
897
1521
2
22.30
37.50
836.25
1406.25
3
9.40
22.20
208.68
492.84
4
9.70
17.50
169.75
306.25
5
0.15
0.64
0.096
0.4096
6
0.28
0.45
0.126
0.2025
7
0.75
2.62
1.965
6.8644
8
0.51
2.36
1.2036
5.5696
9
18.00
32.00
896
1024
10
0.39
0.77
0.3003
0.5929
Total
-
Step 4 of 8
Clearly, from the above table, we have
,
,
,
-
Step 5 of 8
Therefore, the fitted model is
-
Step 6 of 8
(a) The fitted regression (linear) model indicates that the change in the predicted value of LS50 flow-through will increase 0.66 units for a unit increment in LC50 static value and will be -0.78 if all the LC50 static values are zero.
-
Step 7 of 8
(b) The estimator of the flow-through value for a toxicant with an LC50 static value of
is
-
Step 8 of 8
Labels: Chegg, Free Chegg Answer


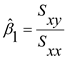

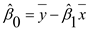













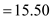






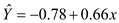



0 Comments:
Post a Comment
Subscribe to Post Comments [Atom]
<< Home